These assets benefit the company for many future years, so it would be improper to expense them immediately when they are purchase. Instead, intangible assets are capitalized when purchased and reported on the balance sheet as a non-current asset. In order to agree with the matching principle, costs are allocated to these assets over the course of their useful life. Remember, amortization expense represents the gradual allocation of an intangible asset’s cost over its useful life.
Automating your way to success: How automation can help relieve accounting staff shortages
Each type of adjustment entry serves a specific purpose and is designed to ensure that financial statements are accurate and complete. The process of recording adjustment entries can be complex, but it is essential for maintaining the integrity of financial statements. When you own and operate a small business, you build up a collection of tangible and intangible assets. Tangible assets include valuable things you can touch, like your business’s building, vehicles, equipment, furniture, etc. Intangible assets are the opposite—they are not physical items.
Ready to transform your procurement processes?

It is calculated by dividing the initial cost of the asset by its estimated useful life, with adjustments made for any salvage value. On the income statement, amortization expense appears as a separate line item, reducing overall net income. It represents the portion of an asset’s cost that has been consumed or used up during a particular period. By including this expense, businesses can reflect the true economic benefit derived from using these assets.
#3. Double declining balance method (DDB)
This can happen due to a lack of attention to detail or a misunderstanding of accounting principles. To avoid this mistake, it is essential to double-check all entries and ensure that they are accurate. Once the need for an adjustment entry has been identified, the bookkeeper or accountant must determine the accounts that need to be adjusted and the amount of the adjustment.
Mistake: Incorrect Accounting Entries
- This method can significantly impact the numbers of EBIT and profit in a given year; therefore, this method is not commonly used.
- The accounting treatment for the amortization of intangible assets is similar to depreciation for tangible assets.
- This means some value of the intangible asset was used in the current accounting period, and the value was therefore reduced.
- Among these are fixed assets, which they use in the long run to generate revenues.
- Here are some best practices to follow when recording amortization expense.
Once the patent reaches the end of its useful life, it has a residual value of $0. For instance, borrowers must be financially prepared for the large amount due at the end of a balloon loan tenure, and a balloon payment loan can be hard to refinance. Failure to pay can significantly hurt the borrower’s credit score and may result in the sale of investments or other assets to cover the outstanding liability. To record the amortization expense, ABC Co. uses the following double entry.
Accrued Revenue
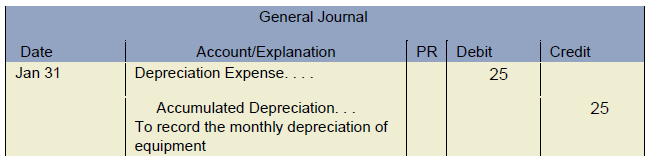
Intangible assets, such as prepaid rent, can be amortized but not depreciated. This is an important distinction that accountants must observe every month-end-close. Amortization expense has a significant impact on financial statements. It reduces net income, which in turn affects profitability ratios such as return on assets (ROA) which journal entry records the amortization of an expense and return on equity (ROE). Additionally, it lowers the carrying value of intangible assets on balance sheets, providing a more accurate reflection of their current worth. The company can make the amortization expense journal entry by debiting the amortization expense account and crediting the accumulated amortization account.
Using this method, an asset value is depreciated twice as fast compared with the straight-line method. Companies can use the schedules to determine the value they should record. However, they can also calculate the value based on the agreement made with the related financial institution. There are mainly two effects of amortization in the financial statements. Different types of amortization exist, including straight-line amortization, declining balance amortization, and sum-of-the-years digit amortization.
You record each payment as an expense, not the entire cost of the loan at once. Goodwill amortization is when the cost of the goodwill of the company is expensed over a specific period. Amortization is usually conducted on a straight-line basis over a 10-year period, as directed by the accounting standards. Many intangibles are amortized under Section 197 of the Internal Revenue Code. This means, for tax purposes, companies need to apply a 15-year useful life when calculating amortization for “section 197 intangibles,” according the to the IRS.

Leave a Reply